Rosales are one major subclade of symbiotic nitrogen fixing plant clade and comprise nine families: Barbeyaceae, Cannabaceae, Dirachmaceae, Elaeagnaceae, Moraceae, Rhamnaceae, Rosaceae, Ulmaceae, and Urticaceae, which includes about 261 genera and 7725 species. These families are morphologically heterogeneous, and had been considered to be distantly related and placed in different orders in traditional classifications. Although the circumscription of Rosales has become clear, interfamily relationships within the order remained ambiguous. In order to resolve this problem, Dr. ZHANG Shudong, Professor LI Dezhu and YI Tingshuang of Kunming Institute of Botany, CAS, and Douglas E. Soltis of University of Florida have reconstructed the phylogeny of this order.
In this study, two nuclear and 10 plastid loci were used to infer phylogenetic relationships among all nine families of Rosales. Rosales were strongly supported as monophyletic; within Rosales all family relationships are well-supported with Rosaceae sister to all other members of the order. Remaining Rosales can be divided into two subclades: 1) Ulmaceae are sister to Cannabaceae plus (Urticaceae + Moraceae); 2) Rhamnaceae are sister to Elaeagnaceae plus (Barbeyaceae + Dirachmaceae). One noteworthy result is that the first strong support for a sister relationship between the enigmatic Dirachmaceae and Barbeyaceae. These two small families have distinct morphologies and potential synapomorphies remain unclear. Future studies should try to identify nonDNA synapomorphies uniting Barbeyaceae with Dirachmaceae.
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant NO. 40830209) and CAS Innovation Program (grant NO. 2007311002) and the Angiosperm Tree of Life Project (NSF EF-0431266).
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1055790311001928
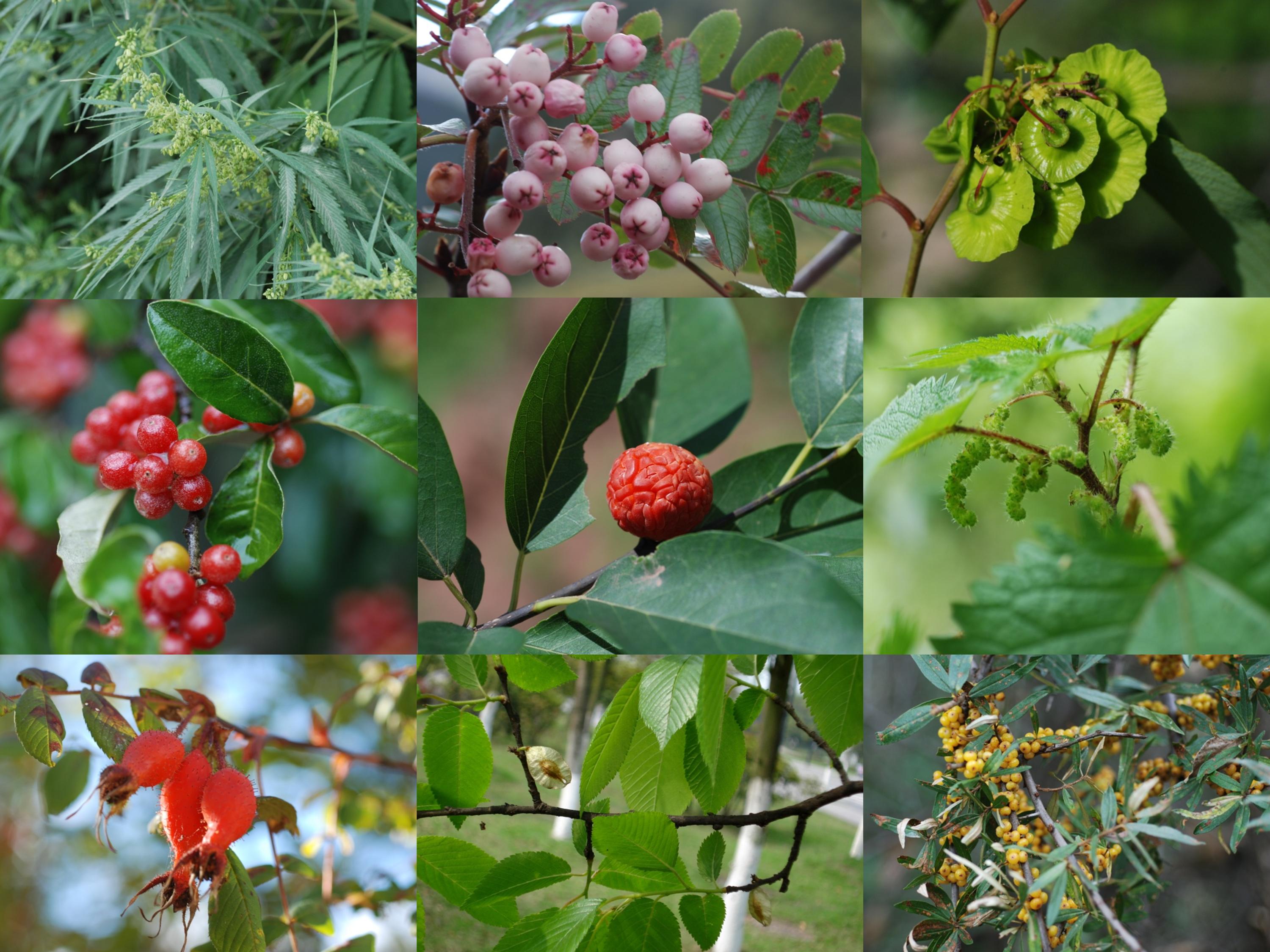

The representative species of nine families of Rosales (image by KIB)
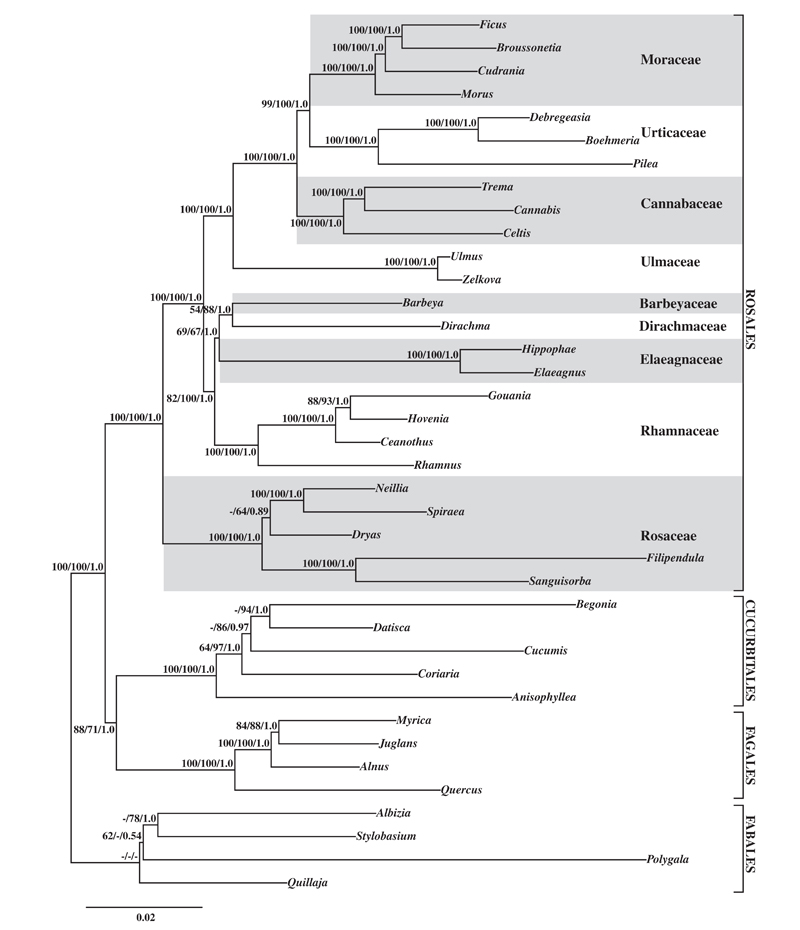
ML tree resulting from GARLI analysis of total evidence dataset (two nuclear genes, 10 plastid genes). The bootstrap values (%) of MP and ML analysis, and PP values ofBI analyses are shown above clades (MPBS/MLBS/PP, dash indicate the branches that are not supported by MPBS, MLBS or PP values). (image by KIB)

