Since the discovery of aspirin as one of nonsterodial anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) more than a century ago, aspirin has become the most widely administered medicine in the treatment of conditions such as pain, fever, and inflammation. In addition to its anti-inflammatory effects, it was reported that long-term use of aspirin could improve many aspects of health status, but the molecular mechanisms remain unclear.
The study on the mechanisms of aspirin-induced lifespan extension on Caenorhabditis elegans had been executed by qin-li wan in LUO Huairong's group,Kunming Institute of Botany. The results showed that aspirin could extend the lifespan of C. elegans, increase its health span and stress resistance. The extension of lifespan by aspirin requires DAF-16/FOXO, AMPK, and LKB1, but not SIR-2.1.Aspirin could not extend the lifespan of mutants of eat-2, clk-1, and isp-1. Aspirin could marginally extend the lifespan of long-live insulin-like receptor mutant daf-2(e1370) III. Taken together, aspirin might act through a dietary restriction-like mechanism, via increasing the AMP:ATP ratio and activating LKB1, subsequently activating AMPK, which stimulate DAF-16 to induce downstream effects through DAF-16 translocation independent manner.
The study “Aspirin extends the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans via AMPK and FOXO/DAF-16 in dietary restriction pathway” had been published in Experimental Gerontology, the link” http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2013.02.020”.
This work was partially supported by the Yunnan provincial government, and the State Key Laboratory of Phytochemistry and Plant Resources in West China, Kunming Institute of Botany.
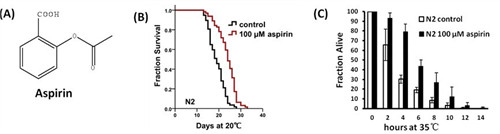
Aspirin extended lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans and improved thermotolerance
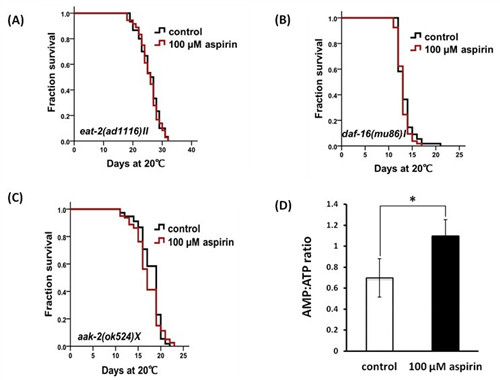
Aspirin acts through a dietary restriction-like mechanism to extend lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans, which requires for DAF/FOXO, AMPK and increases the AMP:ATP ratio.

