The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau lies in the heart of Asia and a steady stream of its glacier melt injects into the top ten rivers in Asia. The effects of climate change exceed the global average. Research found that the higher the more obvious the temperature elevation is. A paper by researcher XU Jianchu, published in Conservation Biology, fully revealed the far-reaching implications of climate warming on water resources, biological diversity, ecotone and the agro-ecological environment as well as providing feedback on global environmental change. The research suggested establishing local and regional scale joint research so as to reduce the uncertainty of assessment impacted by climate change and setting up climate change mitigation and adaptation measures and early warning mechanisms and changing passive adaptation to active adaptation.
At the same time, rubber cultivation is expanding at an alarming rate from southern Yunnan to Southeast Asia Mountains. More than 50 million hectares of mountains have been converted to rubber plantations in China, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam, Cambodia and Myanmar. What will the environmental impact be if large areas of forests turn to rubber plantation? The study co-published on Science by researcher XU Jianchu and National University of Singapore indicated that the large-scale monoculture of rubber trees not only directly threaten biological diversity, causing a reduction of total biomass and carbon sequestration, but also have a negative impact on the hydrological process, especially resulting in the reduction of water table and dry season runoff. The study proposed to inspirit the local residents to protect the existing forest resources through ecological compensation measures and change the situation of monoculture rubber plantations by Agroforestry.

云南南部橡胶种植园
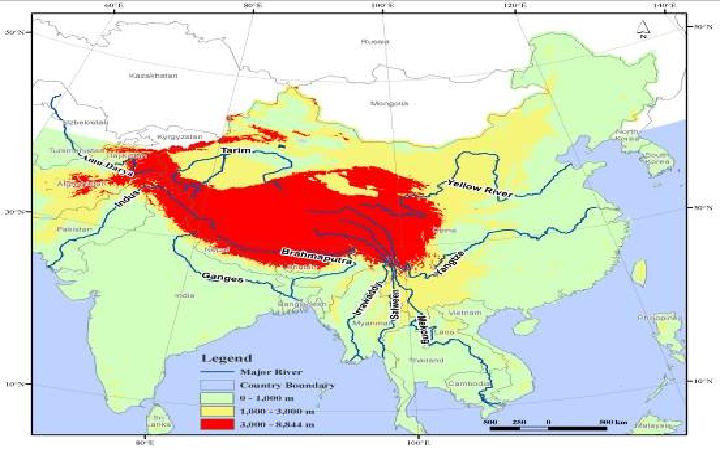
中国海拔分布图




