Southwest China is one of the most important distribution centers of Rhododendron in the world with more than four hundred species. One of the most common Rhododendron species in southwest China is Rhododendron decorum Franch. This is an important ornamental plant and plays an important role in establishment of forests in harsh environments. Ericoid mycorrhiza plays important roles in plant nutrition and ecological adaptation to harsh environments. Therefore, it is valuable to know the mycorrhizal associations of R. decorum in the native habitat.
The diversity of ericoid mycorrhizal fungi isolated from R. decorum in Yunnan, South-West China has been examined for the first time. In total, three hundred hair-root samples were collected from thirteen R. decorum individuals in two adjacent wild population sites and one cultivated population site. A total of 218 slow-growing isolates were obtained, the ability of some of which to form ericoid mycorrhiza was tested in vitro. A total of 125 isolates formed hyphal structures morphologically corresponding to ericoid mycorrhiza, and these were determined by morphological and molecular means to belong to twelve fungal species. There were hardly any differences in species among the three sampled populations. The sequences of several isolates were similar to those of Oidiodendron maius and ericoid mycorrhizal fungi from Helotiales, accounting for 18.4% and 24.8% of the total culturable ericoid mycorrhizal fungi assemblage, respectively.
The paper ‘Diversity of culturable ericoid mycorrhizal fungi of Rhododendron decorum in Yunnan, China’ was published in Mycologia.
http://www.mycologia.org/cgi/content/abstract/103/4/703
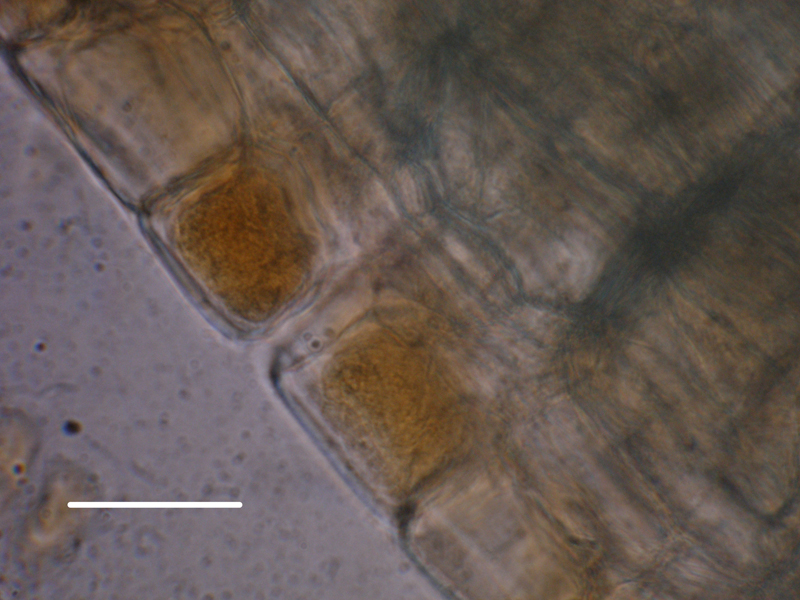
The longitudinal section of mycorrhiza synthesized with Chaetomium sp.. Bar = 100 um (image by TIAN Wei)




