Tribe Gomphostemmateae Scheen & Lindqvist (Lamiaceae: Lamioideae) includes three genera—Bostrychanthera Benth., Gomphostemma Wall. ex Benth. and Chelonopsis Miq., which together comprise about 46 species. Chelonopsis is an East Asian genus and subdivided into two subgenera: subg. Chelonopsis is a Sino-Japanese group while subg. Aequidens is a Sino-Himalaya group. As currently circumscribed, the genus includes 14 species and two varieties, and most species are narrow endemics.
In cooperate with other peers from home and abroad, the research group leading by Dr. PENG Hua from Kunming Institute of Botany , reconstruct the phylogeny of Chelonopsis for the first time by using of two nuclear regions (ITS and ETS) and five plastid loci (psbA-trnH, rps16, trnL intron, trnL-trnF spacer and trnS-trnG). The molecular results indicate that the tribe Gomphostemmateae is monophyletic; Bostrychanthera is embedded in Chelonopsis; and Chelonopsis comprises two clades, one encompassing the taxa of Chelonopsis subg. Chelonopsis and the genus Bostrychanthera and the other consisting of Chelonopsis subg. Aequidens. This split is supported by several morphological characters. These results, which are further strengthened by morphological and cytological data, indicate that Bostrychanthera should be transferred to Chelonopsis. In addition, the results show that within subg. Aequidens, sect. Aequidens and sect. Microphyllum are monophyletic. Furthermore, two major clades are concordant with the Sino-Japanese and Sino-Himalayan distribution patterns.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC: 31100164, 1110103911) and the Main Direction Program of Knowledge Innovation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (grant no. KSCX2-EW-Z-1).
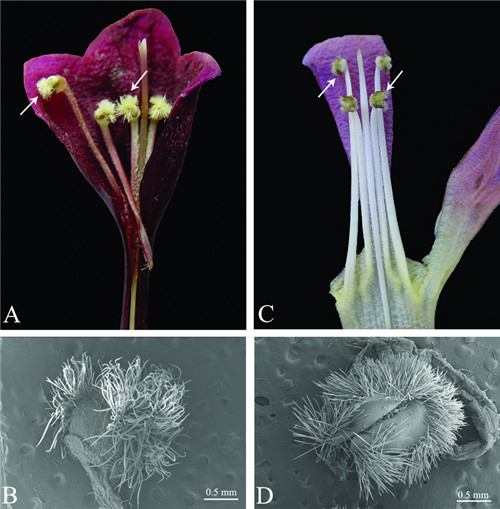

Anther hairs on pollen sacs of Bostrychanthera and Chelonopsis (arrow).
A-B, B. deflexa; C, C. mollissima; D, C. praecox; B, D, SEM micrographs.
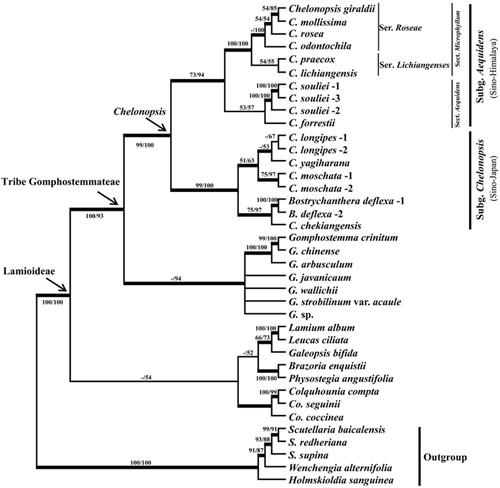
The Bayesian majority-rule consensus tree based on the combined data of nuclear (ITS and ETS) and cpDNA (psbA-trnH, rps16, trnL intron, trnL-trnF spacer and trnS-trnG).
Thick branches have Bayesian posterior probabilities higher than 0.95.
The bootstrap support values higher than 50% in maximum parsimony (MP) and maximum likelihood (RAxML) analyses are shown above the branches in that order.
The infrageneric classification of Chelonopsis follows Wu & Li (1965, 1977)




