Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway plays an important role in embryonic development, cell proliferation, differentiation as well as stem cells maintenance and self-renewal. Abnormal activation of Wnt signaling led to tumorigenesis of colon cancer, and many other malignancies, highlighting it as an important therapeutic target in cancer drug study. Isodon plants have been used in folk medicine to prevent inflammation and gastrointestinal disease for a long time. Previous work suggested that many ent-kaurane diterpenoids (such as Eriocalyxin B, Oridonin etc) isolated from Isodon plants have great therapeutic potentials for cancer and inflammation diseases.
The Professor LI Yan and SUN Handong’s group in Kunming Institute of Botany, found that henryin, an ent-kaurane diterpenoid, isolated from Isodon rubescens var. lushanensis, exhibited selective growth inhibitory effects on human colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting Wnt signaling. The data showed that henryin directly interferes with β-catenin/TCF transcriptional complex interaction and induces the G0/G1 phase arrest in colorectal cancer cells. The structure-activity relationship was also analyzed. Accordingly, henryin, as a novel inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin pathway, could make a promising drug candidate for both the prevention of colorectal cancer as well as a novel therapeutic.
The paper has been published online by the journal of PLoS ONE recently(http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0068525). This work was supported by grants from Major State Basic Research Development Program of China, Natural Science Foundation of China, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Yunnan province.
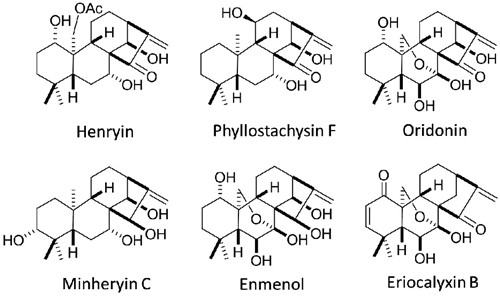
Structures of ent-kaurane diterpenoids
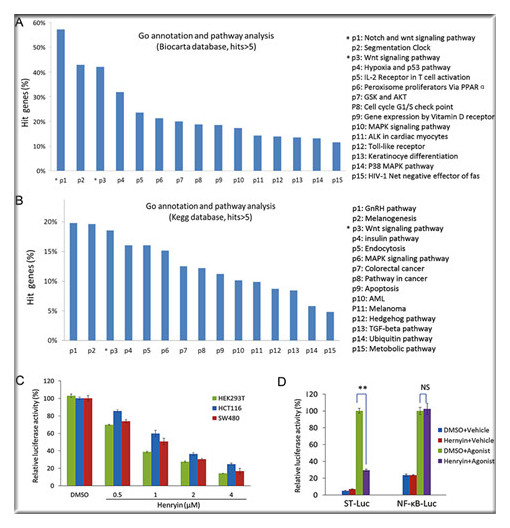
Henryin inhibits Wnt signaling pathway in colorectal cancer cells




