Chukrasia A. Juss. is a medium to large tree genus comprising only C. tabularis and C. tabularis var. velutina, distributed mainly in South and Southeast Asia. The timber of Chukrasia is high-grade wood famous all over the world. Besides, being huge and leafy, Chukrasia is often used as roadside or landscape trees.
Genus Chukrasia excels at generate diverse phragmalin limonoids with novel skeletons, which was frequently reported in literatures, making it a research hot topic in the field of natural products research in the past decade. Recently, research group led by Professor QIU Minghua in Kunming institute of botany, has discovered a series of phragmalin limonoids characterized by C-15/furan ring linkages from the twigs and leaves of C. tabularis. Particularly, two limonoids featuring a C-15/C-20 linkage pattern and the resulting unique 2-oxaspiro[4.4]non-3-ene fragment were obtained (1, 2). Bioassays tests on these compounds demonstrated that 1 was moderately cytotoxic to five tested human cancer cell lines. The research provides new technical data and scientific evidences for further utilizations of twigs and leaves of C. tabularis.
The research is reported online in Organic Letters 2013, 15(15): 3902-3905 (http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ol401650m) titled “Chukfuransins A-D, four new phragmalin limonoids with β-furan ring involved in skeleton reconstruction from Chukrasia tabularis”. The research was financially support by NSFC (No.81202437), the NKIG-CAS (No. KSCX2-YW-G-038;Y1235211Q1), and the MOST(SB2007FY400).

A photograph of Chukrasia tabularis
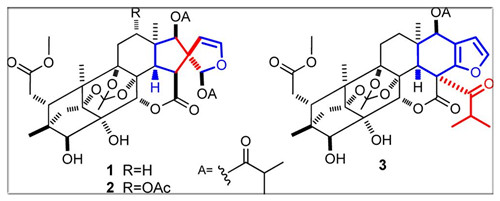
Chemical structure of phragmalin limonods with novel skeleton from Chukrasia tabularis.




