Exploration of natural sources for novel bioactive compounds has been an emerging field of medicine over the past decades, providing drugs or lead compounds of considerable therapeutic potential. This research has provided exciting evidence on the isolation of microbe-derived metabolites having prospective biological activities. Mushrooms have been valued as traditional sources of natural bioactive compounds for many centuries and have been targeted as promising therapeutic agents. Many novel biologically active compounds have been reported as a result of research on medicinal mushrooms. Prof. XU Jianchu form Kunming institute of botany cooperates with Prof. Kevin D Hyde from Institute of Excellence in Fungal Research, Mae Fah Luang University, Thailand to survey the novel bioactive metabolites from mushrooms discovered mainly through the past 10 years and highlights their reported bioactivities and unique chemical diversity, giving potential benefits to novel drug discovery. Moreover, a brief idea on commercially available mushroom products in the market sold as dietary supplements, functional foods and newly discovered patent products. In this review, many novel compounds with bioactivities on anti-oxidant, anti-tumor, anti-diabetic and antimicrobial effects have been illustrated.
The study has shown that numerous novel compounds with anti-oxidant, anti-tumor, anti-diabetic and antimicrobial effects activity from medicinal mushroom have been identified. These benefits are primarily due to the presence of low molecular weight metabolites including triterpenes, phenols, polyketides and high molecular weight polysaccharides, proteins and polysaccharide-protein complexes. And today, nature is the master chemist; bioactive compounds of natural origin have been the most consistent successful source for lead for new drugs. These can improve the comfort of patients’ lives or prevent certain diseases or to support drug treatment in chronic diseases to reduce side effects. Even some potent mycotoxins such as the ergot alkaloids have yielded drugs to treat neurological disorders,such as migraine and mental decline in the elderly, after optimisation by medicinal chemistry. Moreover, despite it is a promising clinical research on chemical investigation of mushroom species for bioactive metabolites. But, today, as the emergence of drug-resistant pathogens, drug-resistant cancer cells and occurrence of various side effects for the currently available drugs is an overwhelming problem of medical concern. Therefore, there is an urgent need in exploration of novel compounds with natural origin and as well as further studies on exact mechanism of action of already identified compounds. Meanwhile, search on their possible mechanism of action would satisfy the urging need for new therapies worldwide.
The entitled paper “Bioactive metabolites from macrofungi: ethnopharmacology, biological activities and chemistry” has been published on Fungal Diversity on 6 November 2013.
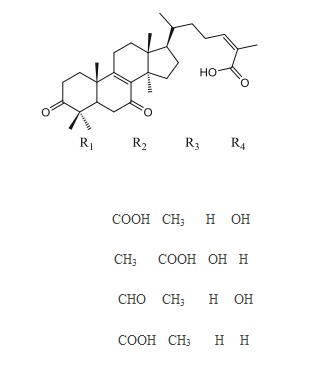
(1)Chemical structure of selected novel triterpenoids with antioxidant polyketides from culture Cyathus stercoreus Figure. 1:
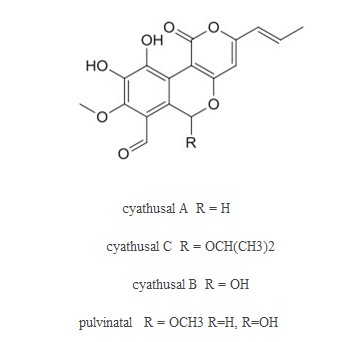
(2)Chemical structure of cordycepin, and cytotoxic terpenoids with anti-viral activity from culture Flammulina velutipes Figure. 2:
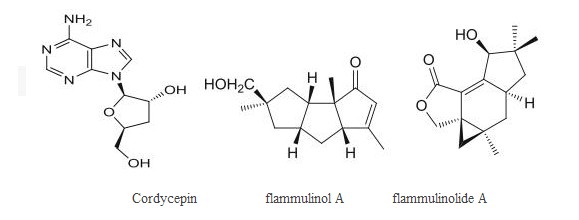
(3)Chemical structures of cordycepin with anti-malarial activity from culture Ganoderma lucidum Figure 3: