Both nitric oxide (NO) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) are important signals that mediate plant response to environmental stimulation. Their role in plants’ allelopathic interactions has also been reported, but the underlying mechanism remains little understood. p-Hydroxybenzoic acid (pHBA) has been proposed to be an allelopathic chemical.
Recently, Dr. GUAN Yanlong advised by Profs. HU Xiangyang, from Kunming institute of botany, found that pHBA at 0.4 mM efficiently suppressed Arabidopsis growth. Meanwhile, pHBA rapidly induced the accumulation of NO and H2O2, where such effect could be reversed by NO or H2O2 metabolism inhibitors or scavengers. Also, pHBA-induced NO and H2O2 could be compromised in NO synthesis mutants noa1, nia1 and nia2, or H2O2 metabolism mutant rbohD/F, but suppressing NO accumulation with a NO synthesis inhibitor or using NO synthesis-related mutants did not reduce pHBA-induced H2O2 accumulation. Furthermore, this work found that the effect of pHBA on allelopathic inhibition of growth was aggravated in NO/H2O2 metabolism-related mutants or reducing NO/H2O2 by different inhibitors, while the addition of an NO/H2O2 donor could partly relieve the inhibitory effect of pHBA on the growth of wild-type . However, adding only a NO donor, but not low concentration of H2O2 as the donor, could relieve the inhibitory effect of pHBA on root growth in NO metabolism mutants, On the basis of these results, this work propose that both NO and H2O2 are important signals that mediate Arabidopsis response to the allelopathic chemical pHBA, where during this process, H2O2 may work upstream of the NO signal.
This work has already published by Physiologia Plantarum (paper link: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24502504 ), and was supported by the Young Academic and Technical Leader Raising Foundation of Yunnan Province (No.2012HB041), the National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (No. 31170256 ).
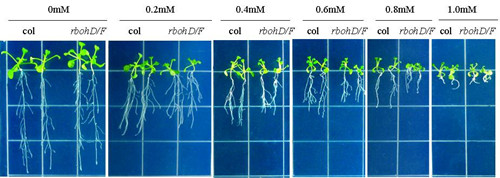
Effect of pHBA on the growth of wild type and H2O2-deficiency mutants
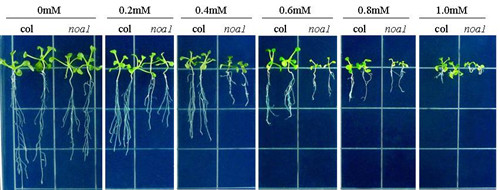
Effect of pHBA on the growth of wild type and NO-deficiency mutants




