Cimicifuga spp. is well-known phytomedicine in world, its extraction have been generally used to treatment for women climacteric syndrome,osteoporosis etc.
Since the triterpenoid alkaloid Cimicifine A discovered in 2007 was cited as hot-off in press in Top journal Natural Product Reports(NPR,2007,24:500) , Prof. Ming-Hua QIU Minghua’s Group at the Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have been focusing on the discovery of anti-tumor triterpenoids from Cimicifuga spp..Recetly, the Group isolated four unprecedented 9,19-cycloartane triterpenoids, cimyunnins A-D (1-4) from the fruit of Cimicifuga yunnanensis. Cimyunnins A-C (1-3) are characterized with an unsual fused cyclopentenone ring G through a new carbon-carbon bond between C-22 and C-26. Cimyunnin D (4) possesses ahighly rearranged -lactone ring F from C-23 to C-27. The new skeleton structures were determined by spectroscopic analysis, X-ray diffraction, and density functional theory calculations.
In vitro and ex vivo studies indicated that cimyunnin A (1) is a potent anti-angiogenic agent. Its activities are comparable to those of sunitinib, which clinically used as first-line angiogenesis inhibitor. Meanwhile, a mechanism study revealed that 1 exerted its effects directly targeting VEGFR2 signaling pathways. Dramatic downregulations of phospho-AKT (Ser473) and phospho-ERK (Thr202/Tyr204), well-known downstream targets of VEGFR2, were observed at 5.0 and 10.0 µM of 1. However, total AKT, ERK, and AKT remain unchanged. Therefore, compound 1 exerted its anti-angiogenic effect through directly targeting VEGFR2 on the surface of endothelial cells and further antagonizing VEGFR2-mediated downstream signaling cascade.
The research published on Scientific Reports: http://www.nature.com/articles/srep09026 by collaborated with Prof. YANG Jing from KIB and Prof. ZHANG Xuhong from Kunming University of Science and Technology (KMST).
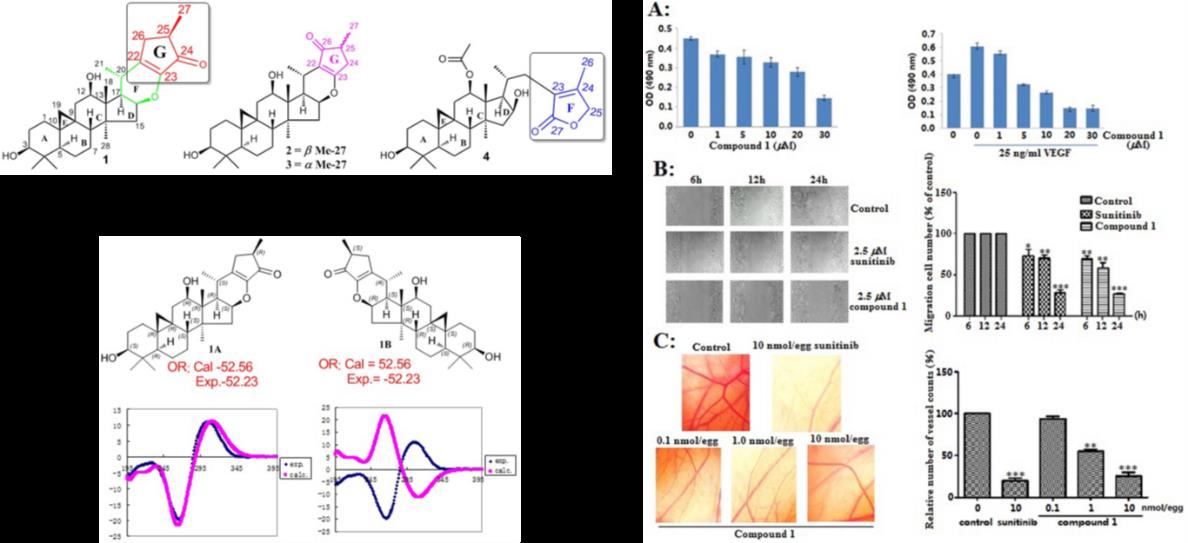
Fig. 1 Discovery of novel Cimyunnins A-D from Cimicifuga yunnanensis and Their Anti-angiogenic Functions (Image by KIB)
Furthermore, ERα/PR/HER2 triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) is a subtype of breast cancer with the poorest prognosis. It is urgent to identify new therapy targets and develop therapeutic drugs for TNBC.
QIU Minghua’s Group also discovered a new inhibitor KHF16 that showed potent anti-cancer activity in multiple TNBC cell lines . Bioactive KHF16 with a six-member epoxy ring formed ether linkage between C16 and C-22 isolated from the rhizomes of C. foetida, its chemical structure were elucidated as24-acetylisodahurinol-3-O-β-D-xylopyranoside.
Further research results showed that KHF16 significantly induces G2/M phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in both MDA-MB-468 and SW527 TNBC cell lines. KHF16 reduces the expression levels of XIAP, Mcl-1, Survivin and Cyclin B1/D1 proteins. Importantly, KHF16 inhibits TNFα-induced IKKα/βphosphorylation, IKBα phosphorylation, p65 nuclear translocation and NF-κB downstream target gene expression, including XIAP, Mcl-1 and Survivin, in TNBC cells. These results suggest that KHF16 may inhibit TNBC by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway.
The research published on Theranostics: http://www.thno.org/v06p0875.htm by by collaborated with Prof. CHEN Ceshi from Kunming Institute of Zoology (KIZ).
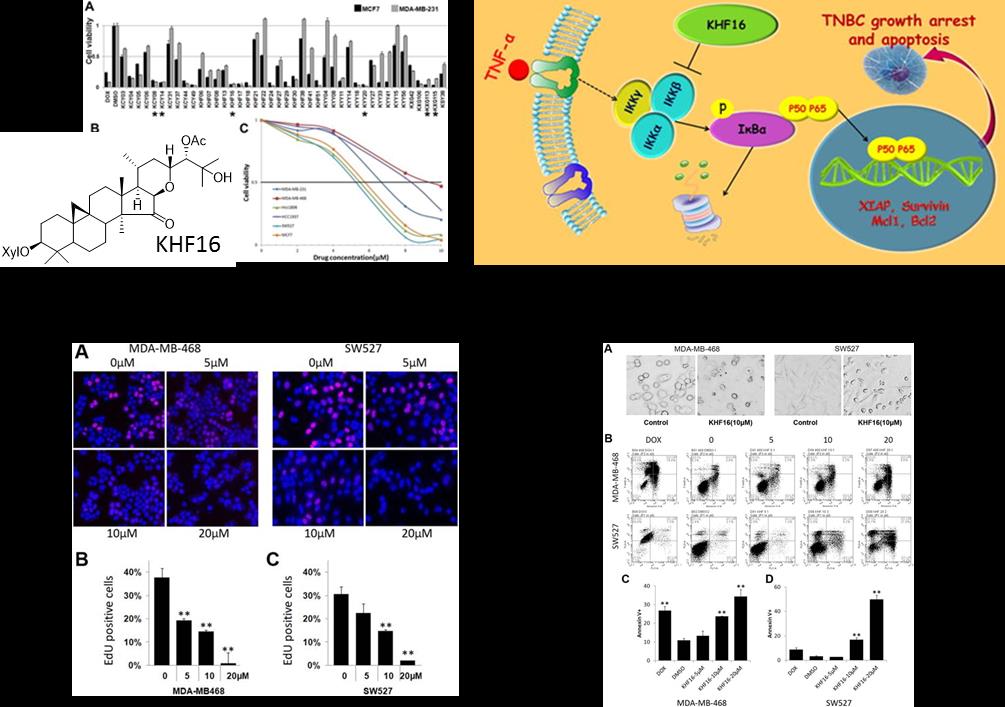
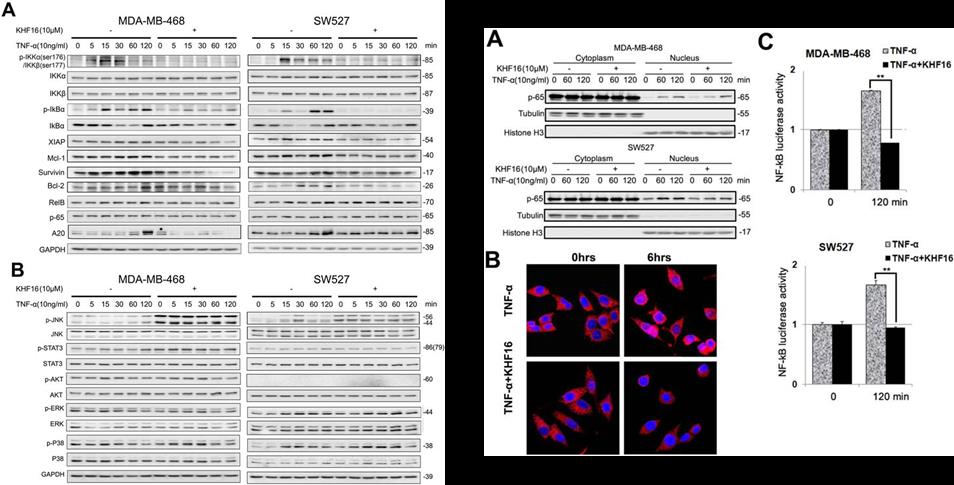
Fig.2 Discovery of TNBC inhibitor KHF16 and its Mechanism of Suppressing Breast Cancer Partially by Inhibiting the NF-kB Signaling Pathway (Image by KIB)
The research also collobarated with Prof. WANG Fei from Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CIB/CAS) isolated a new cycloartane triterpenes, cimiheracleins A (1) from the aerial parts of Cimicifuga heracleifolia. Cimiheracleins A (1) with a lactone in ring A of cimigenol-type triterpene is an important biogenic precursor of 3,4-seco-cimigenol skeleton, shows the inhibition activities in vitro cytotoxicity against human tumor cell lines (HL-60, SMMC-7721, A-549, MCF-7, SW-480) and inhibitory activity with STAT3 signaling pathway.
The research published on Tetrahedron: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/ S0040402015300119
These research works were supported by Program for National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1192604, 8112010819, 81302670 and 81560432).
Contact:
State Key Laboratory of Phytochemistry and Plant Resources in West China
Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Prof. Dr. QIU Minghua
E-mail: mhchiu@mail.kib.ac.cn or qiuminghua@mail.kib.ac.cn




