As an early responder in the surveillance of malignant cells, natural killer (NK) cells play a significant role in the control of transformed cells at the initiation stage through direct cytolysis, therefore NK cell-based immunotherapy is a potential therapeutic strategy for tumor sufferers.
The research groups lead by Prof. LI Yan and Prof. PUNO Pematenzin from Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, found the ent-kaurane diterpenoids, which show wide range of bioactivity, especially antitumor activity, are good candidates as sensitizer agents for NK cells.
The studies revealed the immunomodulatory role of ent-kaurane diterpenoids towards NK cells for the first time.
The research data not only suggest Prxs-I/II as a promising cancer immune therapeutic target, but also provide a compelling rationale for further development of the inhibitor PAA as a sensitizer agent for NK cell-mediated HCC immunotherapy.
The study was published online entitled “Parvifoline AA Promotes Susceptibility of Hepatocarcinoma to Natural Killer cell-mediated Cytolysis by Targeting Peroxiredoxin'' in Cell Chemical Biology.
The results show that a natural ent-kaurane diterpenoid named parvifoline AA (PAA), markedly stimulates the expression of NKG2D ligands on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells, considerably enhancing their recognition and lysis by NK cells.
It involved mechanisms focused on the covalently binding of PAA to the conserved cysteine site of peroxiredoxins I/II (Prxs-I/II), which inhibits their catalytic activity, subsequently activating the ROS/ERK axis and the immunogenicity of HCC toward NK cells. Robust tumor growth inhibition by PAA dependent on NK cell activation was detected in vivo.
The research data not only suggest Prxs-I/II as a promising cancer immune therapeutic target, but also provide a compelling rationale for further development of the inhibitor PAA as a sensitizer agent for NK cell-mediated HCC immunotherapy.
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1402227, 81673329), the Exploitation and Utilization of Abundant Natural Products from Plants from Kunming Institute of Botany (KIB2017009), the 100 Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Program of Recruited Top Talent of Sciences and Technology of Yunnan Province (Y. Li), and the Independent Program of Key Laboratory of Natural Pharmaceutical Chemistry of Yunnan Province.
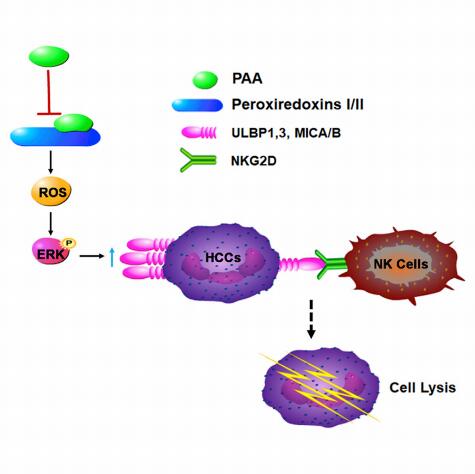
Graphical Abstract (Image by KIB)
Contact:
YANG Mei
General Office
Kunming Institute of Botany, CAS
Email: yangmei@mail.kib.ac.cn
(Editor: YANG Mei)




